Gas laws color by number answers provide an innovative and engaging way to delve into the intricacies of gas laws, making learning an enjoyable and memorable experience. By combining the principles of gas laws with the simplicity of color-by-number activities, this approach offers a unique and effective learning tool that caters to diverse learning styles.
Through interactive tables and bullet points, learners can visualize the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature, gaining a deeper understanding of the behavior of gases under various conditions.
Introduction

Gas laws are a set of mathematical equations that describe the behavior of gases under various conditions. These laws provide a fundamental understanding of the relationships between pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of gas particles in a system.
Color-by-number activities are a fun and engaging way to learn about gas laws. By matching the colors to the corresponding values of pressure, volume, temperature, or the number of gas particles, students can visualize the relationships between these variables and gain a deeper understanding of gas behavior.
Role of Color-by-Number Activities
Color-by-number activities offer several benefits in learning about gas laws:
- Visual Representation:Color-by-number activities provide a visual representation of gas laws, making it easier for students to understand the relationships between pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of gas particles.
- Interactive Learning:These activities are interactive and engaging, allowing students to actively participate in the learning process and reinforce their understanding of gas laws.
- Assessment Tool:Color-by-number activities can also be used as an assessment tool to evaluate students’ comprehension of gas laws.
Boyle’s Law: Gas Laws Color By Number Answers
Boyle’s law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. This means that as the pressure of a gas increases, its volume decreases, and vice versa.
This relationship can be expressed mathematically as follows:
P1V 1= P 2V 2
where:
- P 1is the initial pressure of the gas
- V 1is the initial volume of the gas
- P 2is the final pressure of the gas
- V 2is the final volume of the gas
Boyle’s law can be illustrated using a color-by-number table or bullet points, as shown below:
- If the pressure of a gas is doubled, its volume will be halved.
- If the pressure of a gas is tripled, its volume will be reduced to one-third of its original value.
- If the pressure of a gas is halved, its volume will double.
Charles’s Law
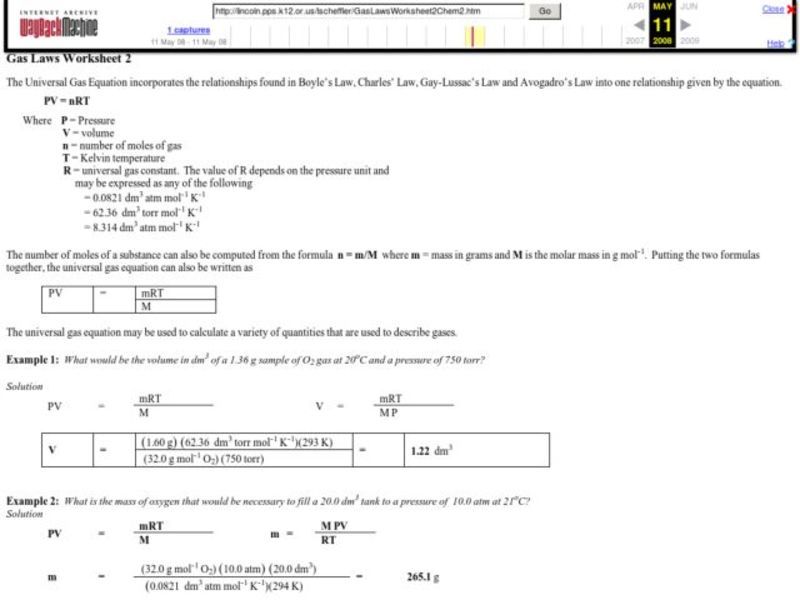
Charles’s law describes the direct relationship between the temperature and volume of a gas at constant pressure. According to Charles’s law, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, meaning that as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume also increases, and vice versa.
Mathematically, Charles’s law can be expressed as follows:
V/T = constant
Where:
- V represents the volume of the gas
- T represents the absolute temperature of the gas
This relationship can be illustrated through a color-by-number table:
| Temperature (K) | Volume (L) |
|---|---|
| 273 | 1 |
| 283 | 1.1 |
| 293 | 1.2 |
| 303 | 1.3 |
| 313 | 1.4 |
Gay-Lussac’s Law
Gay-Lussac’s law, also known as the pressure-temperature law, describes the direct relationship between the pressure and temperature of a gas. It states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature when the volume remains constant.
Mathematically, Gay-Lussac’s law can be expressed as:
P/T = constant
where P is the pressure, T is the absolute temperature, and the constant represents the initial conditions of the gas.
Color-by-Number Table
The following table illustrates the direct relationship between pressure and temperature according to Gay-Lussac’s law:
- If the temperature increases, the pressure increases proportionally.
- If the temperature decreases, the pressure decreases proportionally.
Combined Gas Law
The combined gas law combines Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, and Gay-Lussac’s law into a single equation that describes the behavior of gases under varying conditions of pressure, volume, and temperature.
The combined gas law is expressed as: $$\fracP_1V_1T_1 = \fracP_2V_2T_2$$ where: – P is the pressure of the gas in pascals (Pa) – V is the volume of the gas in cubic meters (m 3) – T is the temperature of the gas in kelvins (K)
The combined gas law can be used to solve a variety of problems involving gases, such as finding the volume of a gas at a different pressure or temperature, or finding the pressure of a gas at a different volume or temperature.
Applications of the Combined Gas Law, Gas laws color by number answers
The combined gas law has a wide range of applications in chemistry and other fields. Some examples include:
- Determining the volume of a gas at a different pressure or temperature. This can be useful in a variety of situations, such as when filling a gas tank or designing a gas-powered engine.
- Finding the pressure of a gas at a different volume or temperature. This can be useful in a variety of situations, such as when designing a gas storage tank or predicting the behavior of a gas in a chemical reaction.
- Predicting the behavior of a gas mixture. The combined gas law can be used to predict the behavior of a gas mixture, such as the pressure, volume, and temperature of the mixture at different conditions.
Q&A
What are gas laws?
Gas laws are a set of principles that describe the behavior of gases under various conditions of pressure, volume, and temperature.
How do gas laws color by number answers help in learning?
Gas laws color by number answers provide a visual and interactive way to understand the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature, making learning more engaging and memorable.