F29 psicosis no orgánica sin especificación – F29 Psychosis Not Otherwise Specified (NOS) is a mental health condition characterized by a range of psychotic symptoms, including hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized speech. It is distinguished from other psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder, by the absence of specific diagnostic criteria for these conditions.
This article provides an overview of F29 NOS, including its diagnostic criteria, clinical features, differential diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis.
The diagnostic criteria for F29 NOS include the presence of at least one positive symptom of psychosis, such as hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized speech, and the absence of criteria for any other specific psychotic disorder. Positive symptoms are those that represent an excess or distortion of normal mental function, such as hallucinations or delusions.
Description of F29 Psychosis Not Otherwise Specified

Define F29 Psychosis Not Otherwise Specified (NOS)
F29 Psychosis Not Otherwise Specified (NOS) is a mental disorder characterized by psychotic symptoms that do not meet the full diagnostic criteria for any other specific psychotic disorder, such as schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder.
Explain the diagnostic criteria for F29 NOS
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), the diagnostic criteria for F29 NOS include:
- The presence of at least one psychotic symptom (hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior)
- The psychotic symptoms cause significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
- The psychotic symptoms are not due to the direct physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse or a medication) or a general medical condition
- The disturbance is not better explained by another mental disorder, such as a mood disorder with psychotic features or a personality disorder with psychotic features
Discuss the prevalence and epidemiology of F29 NOS
F29 NOS is a relatively common mental disorder, with a prevalence of approximately 1% in the general population. It is more common in women than in men and typically begins in early adulthood.
Symptoms of F29 Psychosis Not Otherwise Specified
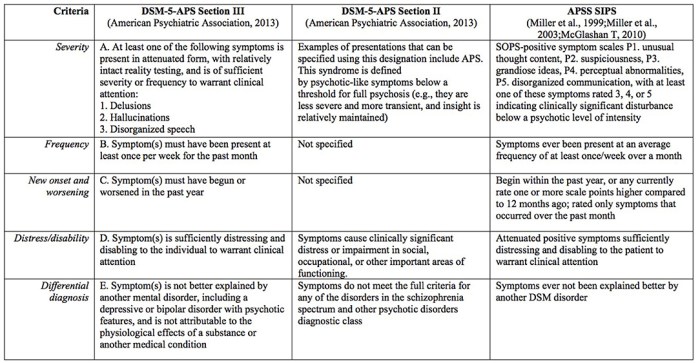
Describe the positive symptoms of F29 NOS, such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized speech
Positive symptoms of F29 NOS are symptoms that represent an excess or distortion of normal functions. They include:
- Hallucinations:Perceptual experiences that occur in the absence of external stimuli, such as hearing voices, seeing visions, or smelling odors
- Delusions:Fixed, false beliefs that are not based in reality, such as believing that one is being persecuted or that one has special powers
- Disorganized speech:Speech that is difficult to understand due to incoherence, derailment, or illogicality
Explain the negative symptoms of F29 NOS, such as social withdrawal, anhedonia, and lack of motivation
Negative symptoms of F29 NOS are symptoms that represent a decrease or loss of normal functions. They include:
- Social withdrawal:A lack of interest in social interactions and a preference for isolation
- Anhedonia:A lack of interest in or pleasure from activities that were once enjoyable
- Lack of motivation:A lack of interest in or drive to engage in goal-directed activities
Discuss the cognitive symptoms of F29 NOS, such as impaired attention, memory, and executive function
Cognitive symptoms of F29 NOS are symptoms that affect thinking and cognition. They include:
- Impaired attention:Difficulty focusing and sustaining attention
- Memory impairment:Difficulty remembering information
- Executive function impairment:Difficulty planning, organizing, and making decisions
Differential Diagnosis of F29 Psychosis Not Otherwise Specified
Explain the differential diagnosis of F29 NOS from other psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder
F29 NOS is differentiated from other psychotic disorders based on the following criteria:
- Schizophrenia:Schizophrenia is characterized by more severe and persistent psychotic symptoms, such as delusions of grandeur or persecution, disorganized speech, and bizarre behavior.
- Schizoaffective disorder:Schizoaffective disorder is characterized by a combination of psychotic symptoms and mood symptoms, such as depression or mania.
Discuss the differential diagnosis of F29 NOS from other mental health conditions, such as mood disorders and personality disorders, F29 psicosis no orgánica sin especificación
F29 NOS is also differentiated from other mental health conditions based on the following criteria:
- Mood disorders:Mood disorders are characterized by disturbances in mood, such as depression or mania, but do not typically include psychotic symptoms.
- Personality disorders:Personality disorders are characterized by inflexible and maladaptive personality traits, but do not typically include psychotic symptoms.
Provide a table summarizing the key differentiating features between F29 NOS and other conditions
| Feature | F29 NOS | Schizophrenia | Schizoaffective disorder | Mood disorders | Personality disorders |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psychotic symptoms | Present | Severe and persistent | Present | Absent | Absent |
| Mood symptoms | Absent | Absent | Present | Present | Absent |
| Personality traits | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Present |
Treatment of F29 Psychosis Not Otherwise Specified
Describe the pharmacological treatment options for F29 NOS, such as antipsychotics and mood stabilizers
Pharmacological treatment options for F29 NOS include:
- Antipsychotics:Antipsychotics are medications that are used to treat psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized speech.
- Mood stabilizers:Mood stabilizers are medications that are used to treat mood symptoms, such as depression or mania.
Explain the psychological treatment options for F29 NOS, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and supportive therapy
Psychological treatment options for F29 NOS include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT):CBT is a type of therapy that helps people to identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to their symptoms.
- Supportive therapy:Supportive therapy is a type of therapy that provides emotional support and helps people to cope with their symptoms.
Discuss the importance of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes both pharmacological and psychological interventions
A comprehensive treatment plan for F29 NOS typically includes both pharmacological and psychological interventions. This approach is most effective in reducing symptoms and improving functioning.
Prognosis of F29 Psychosis Not Otherwise Specified

Explain the factors that influence the prognosis of F29 NOS, such as age of onset, severity of symptoms, and duration of illness
The prognosis of F29 NOS is influenced by a number of factors, including:
- Age of onset:The earlier the onset of symptoms, the worse the prognosis.
- Severity of symptoms:The more severe the symptoms, the worse the prognosis.
- Duration of illness:The longer the duration of illness, the worse the prognosis.
Discuss the long-term outcomes of F29 NOS, including the risk of relapse and the development of chronic disability
The long-term outcomes of F29 NOS vary. Some people recover completely, while others experience persistent symptoms and disability. The risk of relapse is high, especially in people who have had multiple episodes of psychosis.
Provide a table summarizing the prognostic factors and outcomes associated with F29 NOS
| Factor | Prognosis |
|---|---|
| Age of onset | Earlier onset = worse prognosis |
| Severity of symptoms | More severe symptoms = worse prognosis |
| Duration of illness | Longer duration = worse prognosis |
| Risk of relapse | High, especially in people with multiple episodes of psychosis |
| Long-term outcomes | Variable, from complete recovery to persistent symptoms and disability |
Essential Questionnaire: F29 Psicosis No Orgánica Sin Especificación
What is the difference between F29 NOS and schizophrenia?
F29 NOS is a less severe form of psychosis than schizophrenia and does not meet the full diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia. Individuals with F29 NOS may experience fewer symptoms, have a shorter duration of illness, and have a better prognosis than those with schizophrenia.
What are the treatment options for F29 NOS?
Treatment for F29 NOS typically involves a combination of pharmacological and psychological interventions. Pharmacological treatments may include antipsychotic medications to reduce psychotic symptoms and mood stabilizers to manage mood symptoms. Psychological interventions may include cognitive-behavioral therapy to improve coping skills and supportive therapy to provide emotional support and guidance.
What is the prognosis for F29 NOS?
The prognosis for F29 NOS is variable and depends on a range of factors, including age of onset, severity of symptoms, and duration of illness. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and reduce the risk of relapse and chronic disability.
